

Popis
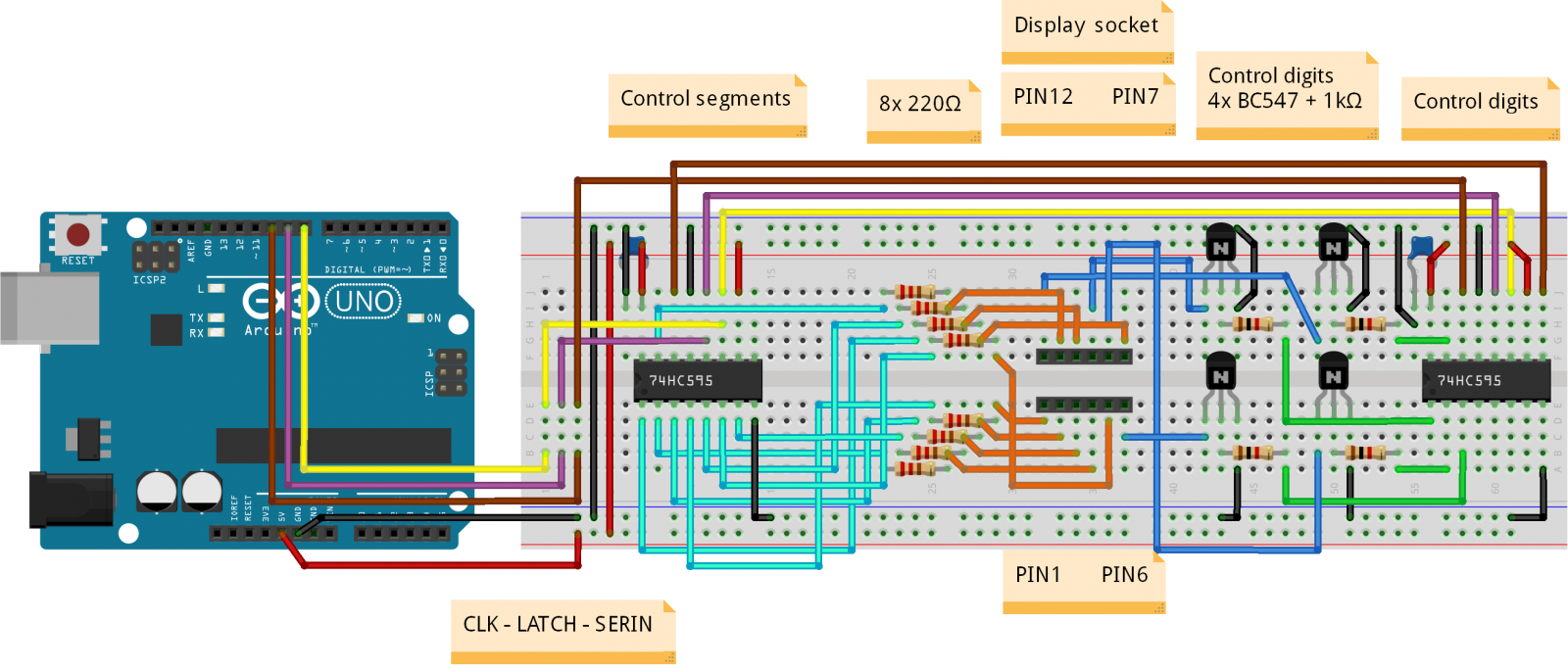
Zobrazení na LED displeji je zařízeno dvěma posuvnými 8-mi bitovými registry 74HC595, kdy jeden slouží ke spínání segmentů na jednom znaku a druhý ke spínání jednotlivých znaků (v tomto zapojení je využito pouze 4 bitů, takže druhá polovina může ovládat další LED). Je použit LED se společnou katodou (GND). Z důvodu malého proudu z pinů arduina je nutné spínat LED přes tranzistory (např. BC547).
Obvod
Příklad kódu
V tomto příkladu je využita knihovna TimerOne.
#include <TimerOne.h>
const int pinLatch = 9;
const int pinClock = 8;
const int pinData = 10;
const int BUFFER_SIZE = 10;
const int DISPLAY_LENGTH = 4;
byte disp[DISPLAY_LENGTH];
byte decimalPointIndex = 255;
byte digits[] = {
B00111111, //0
B00000110, //1
B01011011, //2
B01001111, //3
B01100110, //4
B01101101, //5
B01111101, //6
B00100111, //7
B01111111, //8
B01101111 //9
};
float numbers[] = {
765.4,
765.912,
123,
56.0,
78.1,
12.34,
64.345,
98,
1.4,
5.0,
0.789,
0.1,
.88,
.123,
.4567,
3.7891
};
int numberIndex = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Timer1.initialize(10000);
pinMode(pinLatch, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinClock, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinData, OUTPUT);
setNumber(0);
Timer1.attachInterrupt(showNumber);
}
void loop() {
noInterrupts();
setNumber(numbers[numberIndex]);
Serial.println("OK");
Serial.println(numbers[numberIndex], DEC);
interrupts();
numberIndex++;
if (numberIndex > 15)
numberIndex = 0;
delay(2000);
}
void showNumber() {
byte show = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < DISPLAY_LENGTH; i++) {
byte value = digits[disp[i]];
if (decimalPointIndex == i) value |= 128;
shiftOut(pinData, pinClock, MSBFIRST, (disp[i] > 9 || disp[i] < 0) ? B00000000 : value);
shiftOut(pinData, pinClock, MSBFIRST, B00000001 << i);
digitalWrite(pinLatch, LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLatch, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
shiftOut(pinData, pinClock, LSBFIRST, 0);
shiftOut(pinData, pinClock, LSBFIRST, ~0);
digitalWrite(pinLatch, LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLatch, HIGH);
}
void setNumber(float number) {
if (number >= 10000 || number < 0) return;
byte num[BUFFER_SIZE];
byte dec[BUFFER_SIZE];
byte numCount = 0;
byte decCount = 0;
getWholeNumbers(number, num, numCount);
getDecimals(number, dec, decCount, 4); // find decimal point
decimalPointIndex = (byte) 255;
for (int i = 0; i < DISPLAY_LENGTH; i++) {
disp[i] = (byte) 255;
}
if (number >= 1000.0) {
for (int i = 0; i < DISPLAY_LENGTH; i++) {
disp[i] = num[i];
}
} else if (number >= 100) {
int startIndex = 1;
if (decCount > 0) {
decimalPointIndex = 2;
startIndex = 0;
disp[3] = dec[0];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
disp[i + startIndex] = num[i];
}
} else if (number >= 10) {
int startIndex = 2;
if (decCount > 0) {
int maxDecLength = DISPLAY_LENGTH - numCount;
int numberOfDP = (maxDecLength < decCount) ? maxDecLength : decCount;
startIndex = maxDecLength - numberOfDP;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfDP; i++) {
disp[i + startIndex + 2] = dec[i];
}
decimalPointIndex = (byte)(startIndex + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
disp[i + startIndex] = num[i];
}
} else {
int startIndex = 3;
if (decCount > 0) {
int maxDecLength = DISPLAY_LENGTH - numCount;
int numberOfDP = (maxDecLength < decCount) ? maxDecLength : decCount;
startIndex = maxDecLength - numberOfDP;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfDP; i++) {
disp[i + startIndex + 1] = dec[i];
}
decimalPointIndex = (byte)(startIndex);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
disp[i + startIndex] = num[i];
}
}
}
void getWholeNumbers(float value, byte pData[], byte & count) {
byte n[BUFFER_SIZE];
int p = (int) value;
int l = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < BUFFER_SIZE; i++) {
n[i] = (byte)(p % 10);
p -= n[i];
if (p > 9)
l++;
p /= 10;
}
count = l;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
pData[i] = n[l - 1 - i];
}
}
void getDecimals(float value, byte pData[], byte & count, int maxCount) {
byte n[BUFFER_SIZE];
float f = value;
for (int i = 0; i < BUFFER_SIZE; i++) {
if (i >= maxCount) {
n[i] = 0;
} else {
f *= 10;
n[i] = (byte)(fmod(f, 10));
}
}
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < BUFFER_SIZE; i++) {
if (n[BUFFER_SIZE - 1 - i] == 0) continue;
len = BUFFER_SIZE - i;
break;
}
count = len;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
pData[i] = n[i];
}
}Soubory